Computer Vision
Extracting meaning and building representations of visual objects and events in the world.
Our main research themes cover the areas of deep learning and artificial intelligence for object and action detection, classification and scene understanding, robotic vision and object manipulation, 3D processing and computational geometry, as well as simulation of physical systems to enhance machine learning systems.
Quick Links
-
Researchers

Anoop
Cherian

Tim K.
Marks

Michael J.
Jones

Chiori
Hori

Suhas
Lohit

Jonathan
Le Roux

Kuan-Chuan
Peng

Hassan
Mansour

Matthew
Brand

Moitreya
Chatterjee

Siddarth
Jain

Diego
Romeres

Radu
Corcodel

Pedro
Miraldo

Petros T.
Boufounos

Daniel N.
Nikovski

Ye
Wang

Anthony
Vetro

Gordon
Wichern

William S.
Yerazunis

Toshiaki
Koike-Akino

Dehong
Liu

Arvind
Raghunathan

Abraham P.
Vinod

Pu
(Perry)
Wang
Avishai
Weiss

Stefano
Di Cairano

Yoshiki
Masuyama

Yanting
Ma

Philip V.
Orlik

Joshua
Rapp

Alexander
Schperberg

Huifang
Sun

Yebin
Wang

Kenji
Inomata

Huaizu
Jiang

Jin
Kato

Kaen
Kogashi

Jing
Liu

Lalit
Manam

Kei
Suzuki
-
Awards
-
AWARD Best Paper - Honorable Mention Award at WACV 2021 Date: January 6, 2021
Awarded to: Rushil Anirudh, Suhas Lohit, Pavan Turaga
MERL Contact: Suhas Lohit
Research Areas: Computational Sensing, Computer Vision, Machine LearningBrief- A team of researchers from Mitsubishi Electric Research Laboratories (MERL), Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and Arizona State University (ASU) received the Best Paper Honorable Mention Award at WACV 2021 for their paper "Generative Patch Priors for Practical Compressive Image Recovery".
The paper proposes a novel model of natural images as a composition of small patches which are obtained from a deep generative network. This is unlike prior approaches where the networks attempt to model image-level distributions and are unable to generalize outside training distributions. The key idea in this paper is that learning patch-level statistics is far easier. As the authors demonstrate, this model can then be used to efficiently solve challenging inverse problems in imaging such as compressive image recovery and inpainting even from very few measurements for diverse natural scenes.
- A team of researchers from Mitsubishi Electric Research Laboratories (MERL), Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and Arizona State University (ASU) received the Best Paper Honorable Mention Award at WACV 2021 for their paper "Generative Patch Priors for Practical Compressive Image Recovery".
-
AWARD MERL Researchers win Best Paper Award at ICCV 2019 Workshop on Statistical Deep Learning in Computer Vision Date: October 27, 2019
Awarded to: Abhinav Kumar, Tim K. Marks, Wenxuan Mou, Chen Feng, Xiaoming Liu
MERL Contact: Tim K. Marks
Research Areas: Artificial Intelligence, Computer Vision, Machine LearningBrief- MERL researcher Tim Marks, former MERL interns Abhinav Kumar and Wenxuan Mou, and MERL consultants Professor Chen Feng (NYU) and Professor Xiaoming Liu (MSU) received the Best Oral Paper Award at the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) 2019 Workshop on Statistical Deep Learning in Computer Vision (SDL-CV) held in Seoul, Korea. Their paper, entitled "UGLLI Face Alignment: Estimating Uncertainty with Gaussian Log-Likelihood Loss," describes a method which, given an image of a face, estimates not only the locations of facial landmarks but also the uncertainty of each landmark location estimate.
-
AWARD CVPR 2011 Longuet-Higgins Prize Date: June 25, 2011
Awarded to: Paul A. Viola and Michael J. Jones
Awarded for: "Rapid Object Detection using a Boosted Cascade of Simple Features"
Awarded by: Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR)
MERL Contact: Michael J. Jones
Research Area: Machine LearningBrief- Paper from 10 years ago with the largest impact on the field: "Rapid Object Detection using a Boosted Cascade of Simple Features", originally published at Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2001).
See All Awards for MERL -
-
News & Events
-
TALK [MERL Seminar Series 2026] Zac Manchester presents talk titled Is locomotion really that hard… and other musings on the virtues of simplicity Date & Time: Tuesday, January 20, 2026; 12:00 PM
Speaker: Zac Manchester, MIT
MERL Host: Pedro Miraldo
Research Areas: Computer Vision, Control, Optimization, RoboticsAbstract For decades, legged locomotion was a challenging research topic in robotics. In the last few years, however, both model-based and reinforcement-learning approaches have not only demonstrated impressive performance in laboratory settings, but are now regularly deployed "in the wild." One surprising feature of these successful controllers is how simple they can be. Meanwhile, Art Bryson’s timeless advice to control engineers, “Be wise – linearize,” seems to be increasingly falling out of fashion and at risk of being forgotten by the next generation of practitioners. This talk will discuss several recent works from my group that try to push the limits of how simple locomotion (and, possibly, manipulation) controllers for general-purpose robots can be from several different viewpoints, while also making connections to state-of-the-art generative AI methods like diffusion policies.
For decades, legged locomotion was a challenging research topic in robotics. In the last few years, however, both model-based and reinforcement-learning approaches have not only demonstrated impressive performance in laboratory settings, but are now regularly deployed "in the wild." One surprising feature of these successful controllers is how simple they can be. Meanwhile, Art Bryson’s timeless advice to control engineers, “Be wise – linearize,” seems to be increasingly falling out of fashion and at risk of being forgotten by the next generation of practitioners. This talk will discuss several recent works from my group that try to push the limits of how simple locomotion (and, possibly, manipulation) controllers for general-purpose robots can be from several different viewpoints, while also making connections to state-of-the-art generative AI methods like diffusion policies.
-
NEWS MERL Researchers at NeurIPS 2025 presented 2 conference papers, 5 workshop papers, and organized a workshop. Date: December 2, 2025 - December 7, 2025
Where: San Diego
MERL Contacts: Petros T. Boufounos; Anoop Cherian; Radu Corcodel; Stefano Di Cairano; Chiori Hori; Christopher R. Laughman; Suhas Lohit; Pedro Miraldo; Saviz Mowlavi; Kuan-Chuan Peng; Arvind Raghunathan; Diego Romeres; Abraham P. Vinod; Pu (Perry) Wang
Research Areas: Artificial Intelligence, Computational Sensing, Computer Vision, Control, Data Analytics, Dynamical Systems, Machine Learning, Multi-Physical Modeling, Optimization, Robotics, Signal Processing, Speech & AudioBrief- MERL researchers presented 2 main-conference papers and 5 workshop papers, as well as organized a workshop, at NeurIPS 2025.
Main Conference Papers:
1) Sorachi Kato, Ryoma Yataka, Pu Wang, Pedro Miraldo, Takuya Fujihashi, and Petros Boufounos, "RAPTR: Radar-based 3D Pose Estimation using Transformer", Code available at: https://github.com/merlresearch/radar-pose-transformer
2) Runyu Zhang, Arvind Raghunathan, Jeff Shamma, and Na Li, "Constrained Optimization From a Control Perspective via Feedback Linearization"
Workshop Papers:
1) Yuyou Zhang, Radu Corcodel, Chiori Hori, Anoop Cherian, and Ding Zhao, "SpinBench: Perspective and Rotation as a Lens on Spatial Reasoning in VLMs", NeuriIPS 2025 Workshop on SPACE in Vision, Language, and Embodied AI (SpaVLE) (Best Paper Runner-up)
2) Xiaoyu Xie, Saviz Mowlavi, and Mouhacine Benosman, "Smooth and Sparse Latent Dynamics in Operator Learning with Jerk Regularization", Workshop on Machine Learning and the Physical Sciences (ML4PS)
3) Spencer Hutchinson, Abraham Vinod, François Germain, Stefano Di Cairano, Christopher Laughman, and Ankush Chakrabarty, "Quantile-SMPC for Grid-Interactive Buildings with Multivariate Temporal Fusion Transformers", Workshop on UrbanAI: Harnessing Artificial Intelligence for Smart Cities (UrbanAI)
4) Yuki Shirai, Kei Ota, Devesh Jha, and Diego Romeres, "Sim-to-Real Contact-Rich Pivoting via Optimization-Guided RL with Vision and Touch", Worskhop on Embodied World Models for Decision Making
5) Mark Van der Merwe and Devesh Jha, "In-Context Policy Iteration for Dynamic Manipulation", Workshop on Embodied World Models for Decision Making
Workshop Organized:
MERL members co-organized the Multimodal Algorithmic Reasoning (MAR) Workshop (https://marworkshop.github.io/neurips25/). Organizers: Anoop Cherian (Mitsubishi Electric Research Laboratories), Kuan-Chuan Peng (Mitsubishi Electric Research Laboratories), Suhas Lohit (Mitsubishi Electric Research Laboratories), Honglu Zhou (Salesforce AI Research), Kevin Smith (Massachusetts Institute of Technology), and Joshua B. Tenenbaum (Massachusetts Institute of Technology).
- MERL researchers presented 2 main-conference papers and 5 workshop papers, as well as organized a workshop, at NeurIPS 2025.
See All News & Events for Computer Vision -
-
Research Highlights
-
PS-NeuS: A Probability-guided Sampler for Neural Implicit Surface Rendering -
SAC-GNC: SAmple Consensus for adaptive Graduated Non-Convexity -
TI2V-Zero: Zero-Shot Image Conditioning for Text-to-Video Diffusion Models -
Gear-NeRF: Free-Viewpoint Rendering and Tracking with Motion-Aware Spatio-Temporal Sampling -
Steered Diffusion -
Robust Machine Learning -
Video Anomaly Detection -
MERL Shopping Dataset -
Point-Plane SLAM
-
-
Internships
-
CV0252: Internship - Vital Signs from Video using Computer Vision & AI
-
CA0153: Internship - High-Fidelity Visualization and Simulation for Space Applications
-
CV0223: Internship - Physical Reasoning with Digital Twins
See All Internships for Computer Vision -
-
Openings
See All Openings at MERL -
Recent Publications
- , "Date of publication xxxx 00, 0000, date of current version xxxx 00, 0000. Digital Object Identifier 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.DOI Range Image-Based Implicit Neural Compression for LiDAR Point Clouds", IEEE Access, February 2026.BibTeX TR2026-023 PDF
- @article{Kuwabara2026feb,
- author = {Kuwabara, Akihiro and Kato, Sorachi and Koike-Akino, Toshiaki and Fujihashi, Takuya},
- title = {{Date of publication xxxx 00, 0000, date of current version xxxx 00, 0000. Digital Object Identifier 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.DOI Range Image-Based Implicit Neural Compression for LiDAR Point Clouds}},
- journal = {IEEE Access},
- year = 2026,
- month = feb,
- url = {https://www.merl.com/publications/TR2026-023}
- }
- , "Indoor Multi-View Radar Object Detection via 3D Bounding Box Diffusion", AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, January 2026.BibTeX TR2026-019 PDF Software
- @inproceedings{Yataka2026jan,
- author = {Yataka, Ryoma and Wang, Pu and Boufounos, Petros T. and Takahashi, Ryuhei},
- title = {{Indoor Multi-View Radar Object Detection via 3D Bounding Box Diffusion}},
- booktitle = {AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence},
- year = 2026,
- month = jan,
- url = {https://www.merl.com/publications/TR2026-019}
- }
- , "Robot Confirmation Generation and Action Planning Using Long-context Q-Former Integrated with Multimodal LLM", IEEE Workshop on Automatic Speech Recognition and Understanding (ASRU), December 2025.BibTeX TR2025-167 PDF
- @inproceedings{Hori2025dec,
- author = {Hori, Chiori and Masuyama, Yoshiki and Jain, Siddarth and Corcodel, Radu and Jha, Devesh K. and Romeres, Diego and {Le Roux}, Jonathan},
- title = {{Robot Confirmation Generation and Action Planning Using Long-context Q-Former Integrated with Multimodal LLM}},
- booktitle = {IEEE Workshop on Automatic Speech Recognition and Understanding (ASRU)},
- year = 2025,
- month = dec,
- url = {https://www.merl.com/publications/TR2025-167}
- }
- , "Towards Open-Vocabulary Multimodal 3D Object Detection with Attributes", British Machine Vision Conference (BMVC), November 2025.BibTeX TR2025-162 PDF Video Data Presentation
- @inproceedings{Xiang2025nov,
- author = {{{Xiang, Xinhao and Peng, Kuan-Chuan and Lohit, Suhas and Jones, Michael J. and Zhang, Jiawei}}},
- title = {{{Towards Open-Vocabulary Multimodal 3D Object Detection with Attributes}}},
- booktitle = {British Machine Vision Conference (BMVC)},
- year = 2025,
- month = nov,
- url = {https://www.merl.com/publications/TR2025-162}
- }
- , "DamageEst: Accurate Estimation of Damage for Repair using Additive Manufacturing", Solid Freeform Fabrication Symposium (SFF), November 2025, pp. 1506-1526.BibTeX TR2025-158 PDF Presentation
- @inproceedings{Gambill2025nov,
- author = {{{Gambill, Patrick and Jha, Devesh K. and Krishnamoorthy, Bala and Raghunathan, Arvind and Yerazunis, William S.}}},
- title = {{{DamageEst: Accurate Estimation of Damage for Repair using Additive Manufacturing}}},
- booktitle = {36th Annual International Solid Freeform Fabrication Symposium – An Additive Manufacturing Conference},
- year = 2025,
- pages = {1506--1526},
- month = nov,
- url = {https://www.merl.com/publications/TR2025-158}
- }
- , "Observation-Based Inverse Kinematics for Visual Servo Control", 22nd International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics (ICINCO), October 2025.BibTeX TR2025-153 PDF
- @inproceedings{Nikovski2025oct,
- author = {Nikovski, Daniel N.},
- title = {{Observation-Based Inverse Kinematics for Visual Servo Control}},
- booktitle = {22nd International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics (ICINCO)},
- year = 2025,
- month = oct,
- url = {https://www.merl.com/publications/TR2025-153}
- }
- , "Radar-Conditioned 3D Bounding Box Diffusion for Indoor Human Perception", IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) Workshop, October 2025.BibTeX TR2025-154 PDF Software
- @inproceedings{Yataka2025oct,
- author = {Yataka, Ryoma and Wang, Pu and Boufounos, Petros T. and Takahashi, Ryuhei},
- title = {{Radar-Conditioned 3D Bounding Box Diffusion for Indoor Human Perception}},
- booktitle = {IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) Workshop},
- year = 2025,
- month = oct,
- url = {https://www.merl.com/publications/TR2025-154}
- }
- , "Energy-constrained multi-robot exploration for autonomous map building", IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), DOI: 10.1109/IROS60139.2025.11247332, October 2025, pp. 9154-9161.BibTeX TR2025-131 PDF
- @inproceedings{Karumanchi2025oct,
- author = {Karumanchi, Sambhu and Rokaha, Bhagawan and Schperberg, Alexander and Vinod, Abraham P.},
- title = {{Energy-constrained multi-robot exploration for autonomous map building}},
- booktitle = {IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS)},
- year = 2025,
- pages = {9154--9161},
- month = oct,
- doi = {10.1109/IROS60139.2025.11247332},
- url = {https://www.merl.com/publications/TR2025-131}
- }
- , "Date of publication xxxx 00, 0000, date of current version xxxx 00, 0000. Digital Object Identifier 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.DOI Range Image-Based Implicit Neural Compression for LiDAR Point Clouds", IEEE Access, February 2026.
-
Videos
-
Software & Data Downloads
-
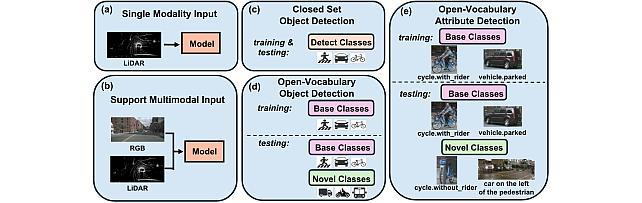
Open Vocabulary Attribute Detection Dataset -
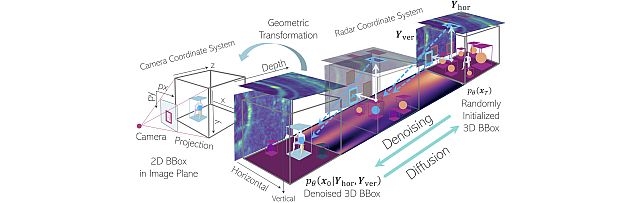
multi-view Radar object dEtection with 3D bounding boX diffusiOn -
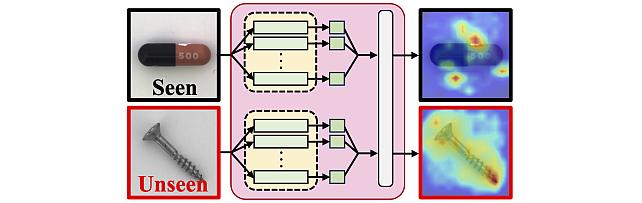
Long-Tailed Online Anomaly Detection dataset -
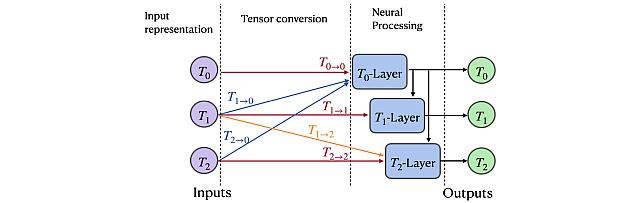
Group Representation Networks -
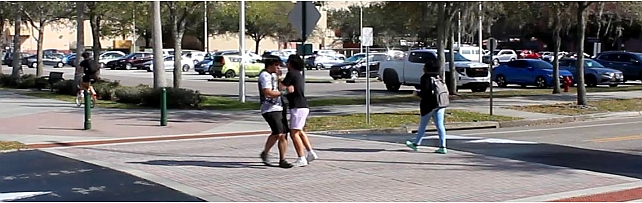
ComplexVAD Dataset -

Zero-Shot Image Conditioning for Text-to-Video Diffusion Models -
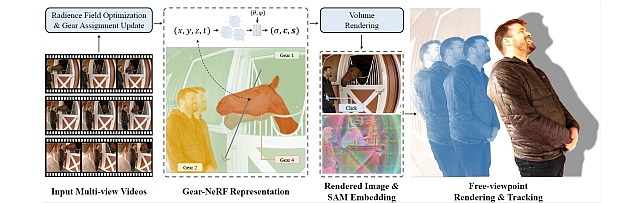
Gear Extensions of Neural Radiance Fields -
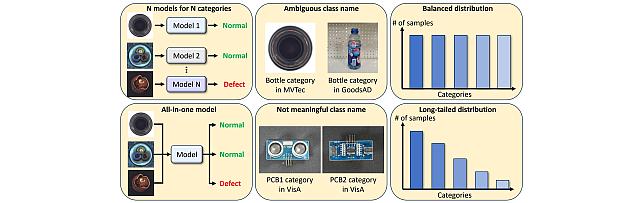
Long-Tailed Anomaly Detection Dataset -

Pixel-Grounded Prototypical Part Networks -

Steered Diffusion -

BAyesian Network for adaptive SAmple Consensus -
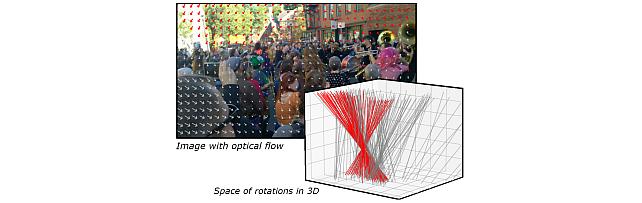
Robust Frame-to-Frame Camera Rotation Estimation in Crowded Scenes
-
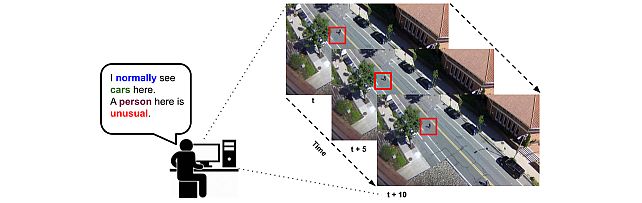
Explainable Video Anomaly Localization -

Simple Multimodal Algorithmic Reasoning Task Dataset -
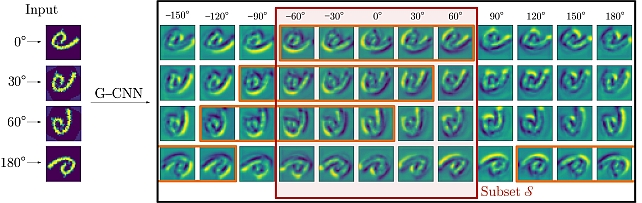
Partial Group Convolutional Neural Networks -
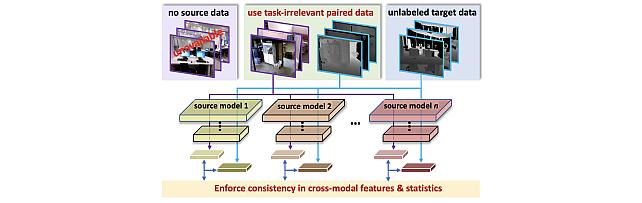
SOurce-free Cross-modal KnowledgE Transfer -
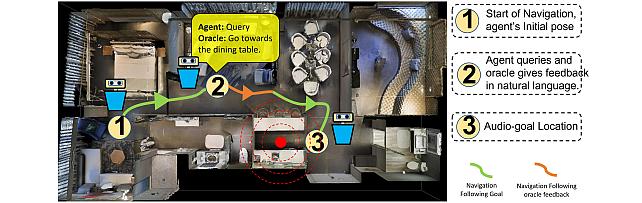
Audio-Visual-Language Embodied Navigation in 3D Environments -
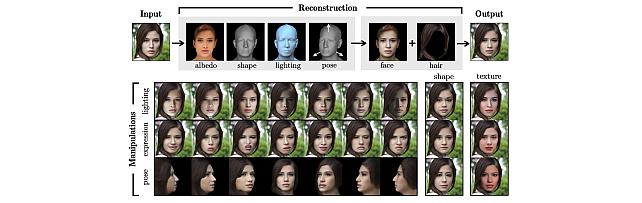
3D MOrphable STyleGAN -
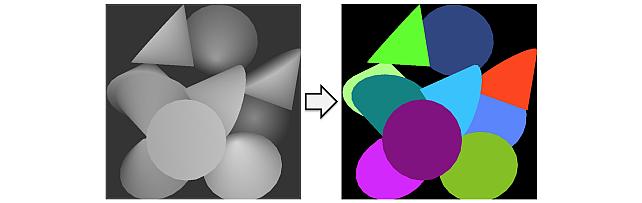
Instance Segmentation GAN -
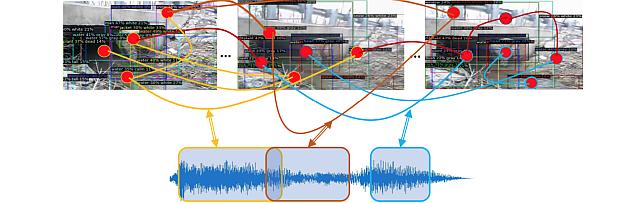
Audio Visual Scene-Graph Segmentor -
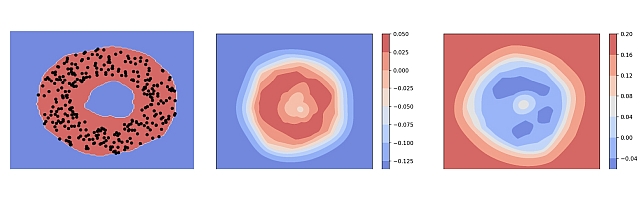
Generalized One-class Discriminative Subspaces -
Generating Visual Dynamics from Sound and Context -

Adversarially-Contrastive Optimal Transport -
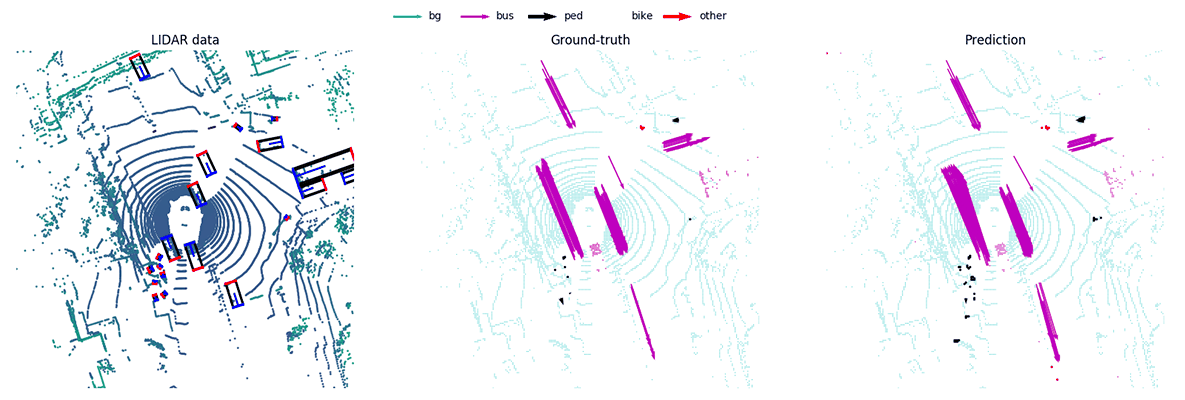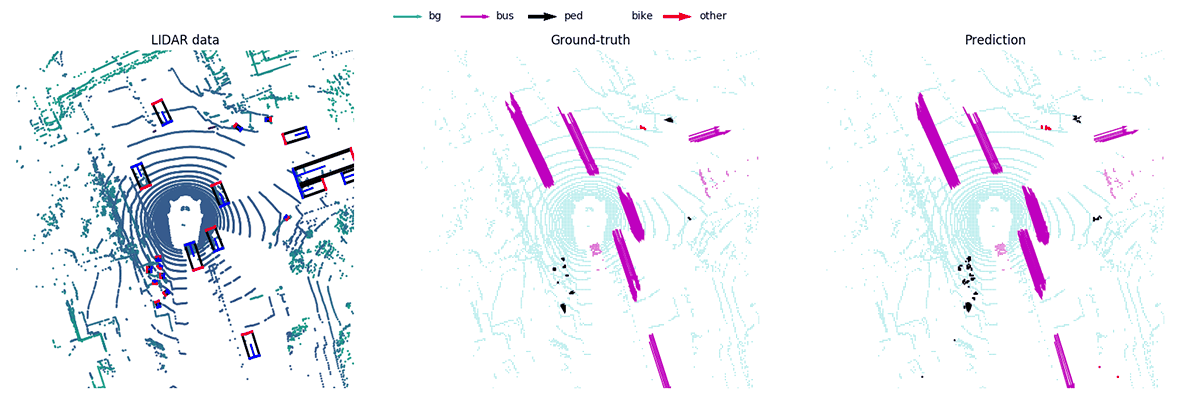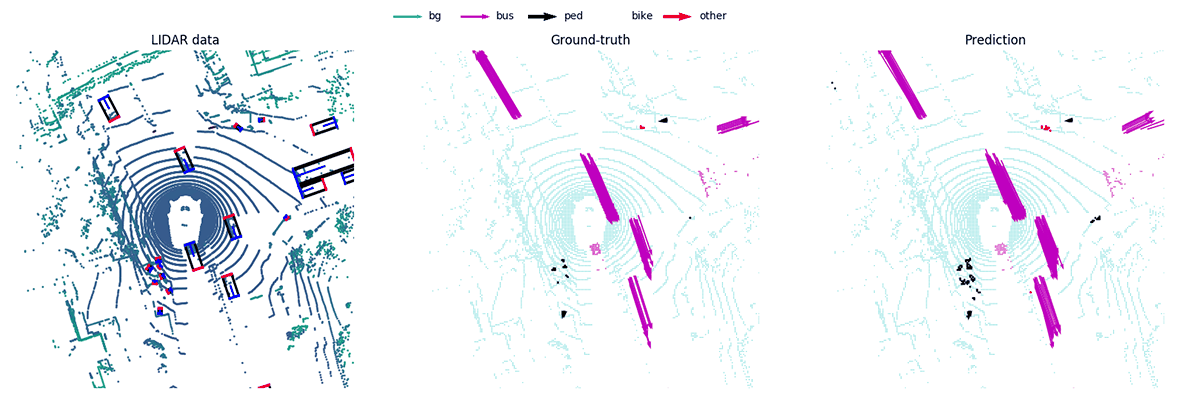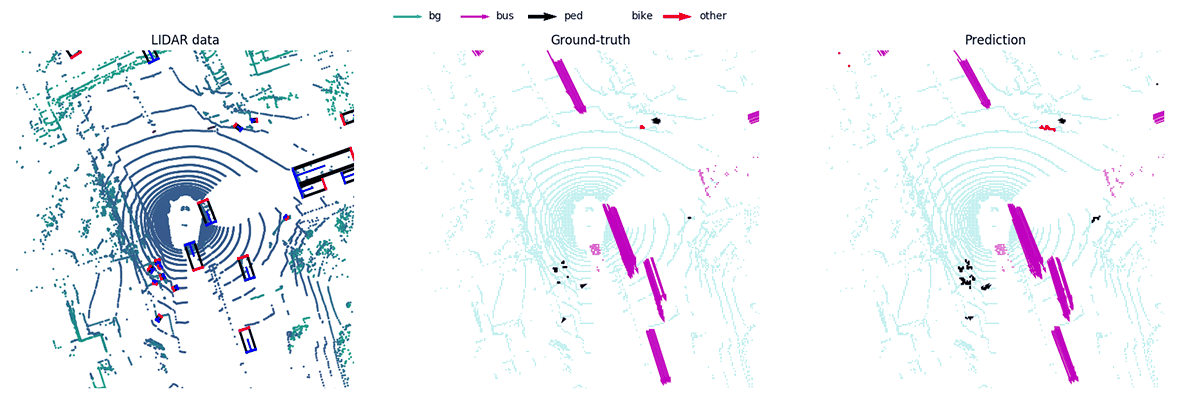
MotionNet -

Street Scene Dataset -
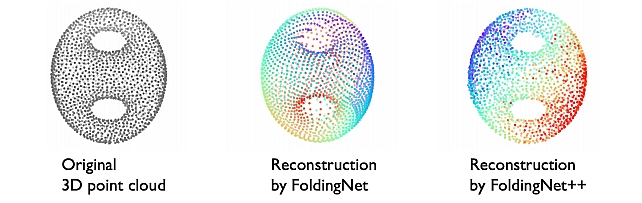
FoldingNet++ -
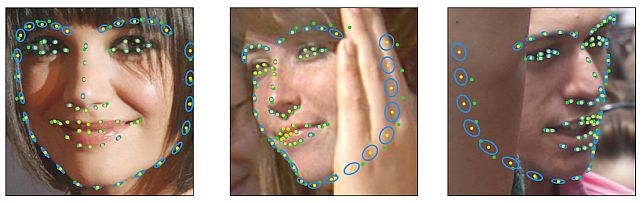
Landmarks’ Location, Uncertainty, and Visibility Likelihood -
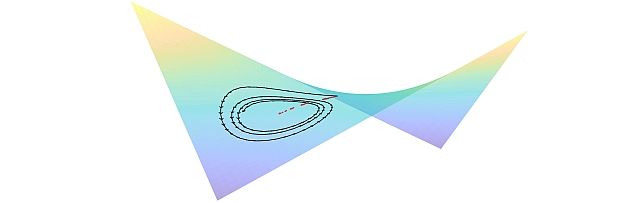
Gradient-based Nikaido-Isoda -
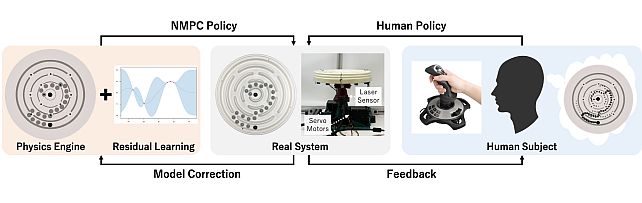
Circular Maze Environment -
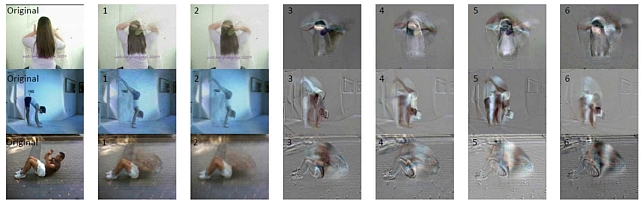
Discriminative Subspace Pooling -
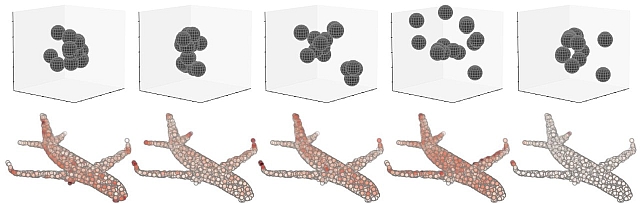
Kernel Correlation Network -

Fast Resampling on Point Clouds via Graphs -
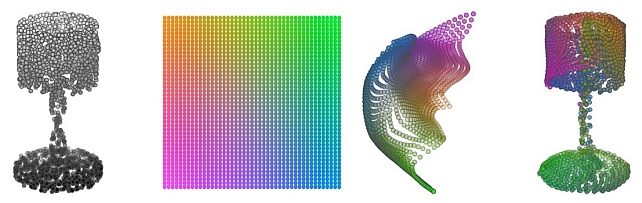
FoldingNet -

MERL Shopping Dataset -
Joint Geodesic Upsampling -

Plane Extraction using Agglomerative Clustering -

MERL BRDF Database -
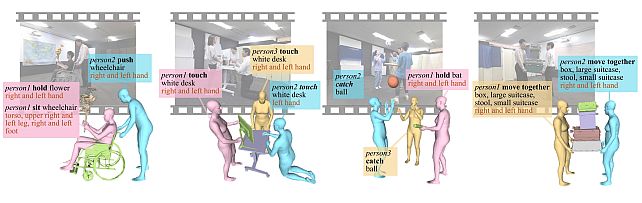
MMHOI Dataset: Modeling Complex 3D Multi-Human Multi-Object Interactions
-