Robotics
Where hardware, software and machine intelligence come together.
Our research is interdisciplinary and focuses on sensing, planning, reasoning, and control of single and multi-agent systems, including both manipulation and mobile robots. We strive to develop algorithms and methods for factory automation, smart building and transportation applications using machine learning, computer vision, RF/optical sensing, wireless communications, control theory and signal processing. Key research themes include bin picking and object manipulation, sensing and mapping of indoor areas, coordinated control of robot swarms, as well as robot learning and simulation.
Quick Links
-
Researchers

Diego
Romeres

Daniel N.
Nikovski

Stefano
Di Cairano

Siddarth
Jain

Arvind
Raghunathan

Radu
Corcodel

Yebin
Wang

William S.
Yerazunis

Toshiaki
Koike-Akino

Abraham P.
Vinod

Chiori
Hori

Avishai
Weiss

Tim K.
Marks

Jonathan
Le Roux

Scott A.
Bortoff

Anoop
Cherian

Alexander
Schperberg

Ye
Wang

Bingnan
Wang

Matthew
Brand

Pedro
Miraldo

Philip V.
Orlik

Purnanand
Elango

Abraham
Goldsmith

Jianlin
Guo

Jing
Liu

Hassan
Mansour

Yoshiki
Masuyama

Saviz
Mowlavi

Zhaolin
Ren

Anthony
Vetro

Kei
Suzuki
-
Awards
-
AWARD University of Padua and MERL team wins the AI Olympics with RealAIGym competition at IROS24 Date: October 17, 2024
Awarded to: Niccolò Turcato, Alberto Dalla Libera, Giulio Giacomuzzo, Ruggero Carli, Diego Romeres
MERL Contact: Diego Romeres
Research Areas: Artificial Intelligence, Dynamical Systems, Machine Learning, RoboticsBrief- The team composed of the control group at the University of Padua and MERL's Optimization and Robotic team ranked 1st out of the 4 finalist teams that arrived to the 2nd AI Olympics with RealAIGym competition at IROS 24, which focused on control of under-actuated robots. The team was composed by Niccolò Turcato, Alberto Dalla Libera, Giulio Giacomuzzo, Ruggero Carli and Diego Romeres. The competition was organized by the German Research Center for Artificial Intelligence (DFKI), Technical University of Darmstadt and Chalmers University of Technology.
The competition and award ceremony was hosted by IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS) on October 17, 2024 in Abu Dhabi, UAE. Diego Romeres presented the team's method, based on a model-based reinforcement learning algorithm called MC-PILCO.
- The team composed of the control group at the University of Padua and MERL's Optimization and Robotic team ranked 1st out of the 4 finalist teams that arrived to the 2nd AI Olympics with RealAIGym competition at IROS 24, which focused on control of under-actuated robots. The team was composed by Niccolò Turcato, Alberto Dalla Libera, Giulio Giacomuzzo, Ruggero Carli and Diego Romeres. The competition was organized by the German Research Center for Artificial Intelligence (DFKI), Technical University of Darmstadt and Chalmers University of Technology.
-
AWARD Honorable Mention Award at NeurIPS 23 Instruction Workshop Date: December 15, 2023
Awarded to: Lingfeng Sun, Devesh K. Jha, Chiori Hori, Siddharth Jain, Radu Corcodel, Xinghao Zhu, Masayoshi Tomizuka and Diego Romeres
MERL Contacts: Radu Corcodel; Chiori Hori; Siddarth Jain; Diego Romeres
Research Areas: Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, RoboticsBrief- MERL Researchers received an "Honorable Mention award" at the Workshop on Instruction Tuning and Instruction Following at the NeurIPS 2023 conference in New Orleans. The workshop was on the topic of instruction tuning and Instruction following for Large Language Models (LLMs). MERL researchers presented their work on interactive planning using LLMs for partially observable robotic tasks during the oral presentation session at the workshop.
-
AWARD Joint University of Padua-MERL team wins Challenge 'AI Olympics With RealAIGym' Date: August 25, 2023
Awarded to: Alberto Dalla Libera, Niccolo' Turcato, Giulio Giacomuzzo, Ruggero Carli, Diego Romeres
MERL Contact: Diego Romeres
Research Areas: Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, RoboticsBrief- A joint team consisting of members of University of Padua and MERL ranked 1st in the IJCAI2023 Challenge "Al Olympics With RealAlGym: Is Al Ready for Athletic Intelligence in the Real World?". The team was composed by MERL researcher Diego Romeres and a team from University Padua (UniPD) consisting of Alberto Dalla Libera, Ph.D., Ph.D. Candidates: Niccolò Turcato, Giulio Giacomuzzo and Prof. Ruggero Carli from University of Padua.
The International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI) is a premier gathering for AI researchers and organizes several competitions. This year the competition CC7 "AI Olympics With RealAIGym: Is AI Ready for Athletic Intelligence in the Real World?" consisted of two stages: simulation and real-robot experiments on two under-actuated robotic systems. The two robotics systems were treated as separate tracks and one final winner was selected for each track based on specific performance criteria in the control tasks.
The UniPD-MERL team competed and won in both tracks. The team's system made strong use of a Model-based Reinforcement Learning algorithm called (MC-PILCO) that we recently published in the journal IEEE Transaction on Robotics.
- A joint team consisting of members of University of Padua and MERL ranked 1st in the IJCAI2023 Challenge "Al Olympics With RealAlGym: Is Al Ready for Athletic Intelligence in the Real World?". The team was composed by MERL researcher Diego Romeres and a team from University Padua (UniPD) consisting of Alberto Dalla Libera, Ph.D., Ph.D. Candidates: Niccolò Turcato, Giulio Giacomuzzo and Prof. Ruggero Carli from University of Padua.
See All Awards for Robotics -
-
News & Events
-
TALK [MERL Seminar Series 2026] Zac Manchester presents talk titled Is locomotion really that hard… and other musings on the virtues of simplicity Date & Time: Tuesday, January 20, 2026; 12:00 PM
Speaker: Zac Manchester, MIT
MERL Host: Pedro Miraldo
Research Areas: Computer Vision, Control, Optimization, RoboticsAbstract For decades, legged locomotion was a challenging research topic in robotics. In the last few years, however, both model-based and reinforcement-learning approaches have not only demonstrated impressive performance in laboratory settings, but are now regularly deployed "in the wild." One surprising feature of these successful controllers is how simple they can be. Meanwhile, Art Bryson’s timeless advice to control engineers, “Be wise – linearize,” seems to be increasingly falling out of fashion and at risk of being forgotten by the next generation of practitioners. This talk will discuss several recent works from my group that try to push the limits of how simple locomotion (and, possibly, manipulation) controllers for general-purpose robots can be from several different viewpoints, while also making connections to state-of-the-art generative AI methods like diffusion policies.
For decades, legged locomotion was a challenging research topic in robotics. In the last few years, however, both model-based and reinforcement-learning approaches have not only demonstrated impressive performance in laboratory settings, but are now regularly deployed "in the wild." One surprising feature of these successful controllers is how simple they can be. Meanwhile, Art Bryson’s timeless advice to control engineers, “Be wise – linearize,” seems to be increasingly falling out of fashion and at risk of being forgotten by the next generation of practitioners. This talk will discuss several recent works from my group that try to push the limits of how simple locomotion (and, possibly, manipulation) controllers for general-purpose robots can be from several different viewpoints, while also making connections to state-of-the-art generative AI methods like diffusion policies.
-
NEWS MERL Researcher Diego Romeres Collaborates with Mitsubishi Electric and University of Padua to Advance Physics-Embedded AI for Predictive Equipment Maintenance Date: December 10, 2025
MERL Contact: Diego Romeres
Research Areas: Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, RoboticsBrief- Mitsubishi Electric Research Laboratories (MERL) researchers, together with collaborators at Mitsubishi Electric’s Information Technology R&D Center in Kamakura, Kanagawa Prefecture, Japan, and the Department of Information Engineering at the University of Padua, have developed a cutting-edge physics-embedded AI technology that substantially improves the accuracy of equipment degradation estimation using minimal training data. This collaborative effort has culminated in a press release by Mitsubishi Electric Corporation announcing the new AI technology as part of its Neuro-Physical AI initiative under the Maisart program.
The interdisciplinary team, including MERL Senior Principal Research Scientist and Team Leader Diego Romeres and University of Padua researchers Alberto Dalla Libera and Giulio Giacomuzzo, combined expertise in machine learning, physical modeling, and real-world industrial systems to embed physics-based models directly into AI frameworks. By training AI with theoretical physical laws and real operational data, the resulting system delivers reliable degradation estimates on the torque of robotic arms even with limited datasets. This result addresses key challenges in preventive maintenance for complex manufacturing environments and supports reduced downtime, maintained quality, and lower lifecycle costs.
The successful integration of these foundational research efforts into Mitsubishi Electric’s business-scale AI solutions exemplifies MERL’s commitment to translating fundamental innovation into real-world impact.
- Mitsubishi Electric Research Laboratories (MERL) researchers, together with collaborators at Mitsubishi Electric’s Information Technology R&D Center in Kamakura, Kanagawa Prefecture, Japan, and the Department of Information Engineering at the University of Padua, have developed a cutting-edge physics-embedded AI technology that substantially improves the accuracy of equipment degradation estimation using minimal training data. This collaborative effort has culminated in a press release by Mitsubishi Electric Corporation announcing the new AI technology as part of its Neuro-Physical AI initiative under the Maisart program.
See All News & Events for Robotics -
-
Research Highlights
-
Internships
-
CV0221: Internship - Robust Estimation for Computer Vision
-
CV0223: Internship - Physical Reasoning with Digital Twins
-
CI0286: Internship - Agentic AI
See All Internships for Robotics -
-
Openings
See All Openings at MERL -
Recent Publications
- , "Reinforcement Learning for Robust Athletic Intelligence: Lessons from the 2nd “AI Olympics with RealAIGym” Competition", IEEE Robotics & Automation Magazine, January 2026.BibTeX TR2026-013 PDF
- @article{Wiebe2026jan,
- author = {{{Wiebe, Felix and Turcato, Niccolò and Dalla Libera, Alberto and Seong Bjorn Choe, Jean and Choi, Bumkyu and Faust, Tim Lukas and Maraqten, Habib and Aghadavoodi, Erfan and Cali, Marco and Sinigaglia, Alberto and Giacomuzzo, Giulio and Carli, Ruggero and Romeres, Diego and Kim, Jong-kook and Susto, Gian Antonio and Vyas, Shubham and Mronga, Dennis and Belousov, Boris and Peters, Jan and Kirchner, Frank and Kumar, Shivesh}}},
- title = {{{Reinforcement Learning for Robust Athletic Intelligence: Lessons from the 2nd “AI Olympics with RealAIGym” Competition}}},
- journal = {IEEE Robotics \& Automation Magazine},
- year = 2026,
- month = jan,
- url = {https://www.merl.com/publications/TR2026-013}
- }
- , "Learning Non-prehensile Manipulation with Force and Vision Feedback Using Optimization-based Demonstrations", IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, January 2026.BibTeX TR2026-011 PDF Video
- @article{Shirai2026jan,
- author = {Shirai, Yuki and Ota, Kei and Jha, Devesh K. and Romeres, Diego},
- title = {{Learning Non-prehensile Manipulation with Force and Vision Feedback Using Optimization-based Demonstrations}},
- journal = {IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters},
- year = 2026,
- month = jan,
- url = {https://www.merl.com/publications/TR2026-011}
- }
- , "Real-time Human Progress Estimation with Online Dynamic Time Warping for Collaborative Robotics", Frontiers, December 2025.BibTeX TR2025-173 PDF
- @article{DeLazzari2025dec,
- author = {De Lazzari, Davide and Terreran, Matteo and Giacomuzzo, Giulio and Jain, Siddarth and Falco, Pietro and Carli, Ruggero and Ghidoni, Stefano and Romeres, Diego},
- title = {{Real-time Human Progress Estimation with Online Dynamic Time Warping for Collaborative Robotics}},
- journal = {Frontiers},
- year = 2025,
- month = dec,
- url = {https://www.merl.com/publications/TR2025-173}
- }
- , "Simultaneous Extrinsic Contact and In-Hand Pose Estimation via Distributed Tactile Sensing", IEEE RA-L, December 2025.BibTeX TR2026-002 PDF
- @article{VanderMerwe2025dec2,
- author = {Van der Merwe, Mark and Ota, Kei and Berenson, Dmitry and Fazeli, Nima and Jha, Devesh K.},
- title = {{Simultaneous Extrinsic Contact and In-Hand Pose Estimation via Distributed Tactile Sensing}},
- journal = {IEEE RA-L},
- year = 2025,
- month = dec,
- url = {https://www.merl.com/publications/TR2026-002}
- }
- , "Motion Planning for Information Acquisition via Continuous-time Successive Convexification", IEEE Conference on Decision and Control (CDC), December 2025.BibTeX TR2025-170 PDF
- @inproceedings{Uzun2025dec,
- author = {Uzun, Samet and Acikmese, Behcet and {Di Cairano}, Stefano},
- title = {{Motion Planning for Information Acquisition via Continuous-time Successive Convexification}},
- booktitle = {IEEE Control Systems Letters},
- year = 2025,
- month = dec,
- url = {https://www.merl.com/publications/TR2025-170}
- }
- , "Robot Confirmation Generation and Action Planning Using Long-context Q-Former Integrated with Multimodal LLM", IEEE Workshop on Automatic Speech Recognition and Understanding (ASRU), December 2025.BibTeX TR2025-167 PDF
- @inproceedings{Hori2025dec,
- author = {Hori, Chiori and Masuyama, Yoshiki and Jain, Siddarth and Corcodel, Radu and Jha, Devesh K. and Romeres, Diego and {Le Roux}, Jonathan},
- title = {{Robot Confirmation Generation and Action Planning Using Long-context Q-Former Integrated with Multimodal LLM}},
- booktitle = {IEEE Workshop on Automatic Speech Recognition and Understanding (ASRU)},
- year = 2025,
- month = dec,
- url = {https://www.merl.com/publications/TR2025-167}
- }
- , "Sim-to-Real Contact-Rich Pivoting via Optimization-Guided RL with Vision and Touch", Embodied World Models for Decision Making, NeurIPS Workshop, December 2025.BibTeX TR2025-169 PDF Video
- @inproceedings{Shirai2025dec,
- author = {Shirai, Yuki and Ota, Kei and Jha, Devesh K. and Romeres, Diego},
- title = {{Sim-to-Real Contact-Rich Pivoting via Optimization-Guided RL with Vision and Touch}},
- booktitle = {NeurIPS 2025 Workshop on Embodied World Models for Decision Making},
- year = 2025,
- month = dec,
- url = {https://www.merl.com/publications/TR2025-169}
- }
- , "AxisBench: What Can Go Wrong in VLMs’ Spatial Reasoning?", Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS) workshop, December 2025.BibTeX TR2025-168 PDF
- @inproceedings{Zhang2025dec2,
- author = {{{Zhang, Yuyou and Corcodel, Radu and Hori, Chiori and Cherian, Anoop and Zhao, Ding}}},
- title = {{{AxisBench: What Can Go Wrong in VLMs’ Spatial Reasoning?}}},
- booktitle = {Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS) workshop},
- year = 2025,
- month = dec,
- url = {https://www.merl.com/publications/TR2025-168}
- }
- , "Reinforcement Learning for Robust Athletic Intelligence: Lessons from the 2nd “AI Olympics with RealAIGym” Competition", IEEE Robotics & Automation Magazine, January 2026.
-
Videos
-
Software & Data Downloads
-
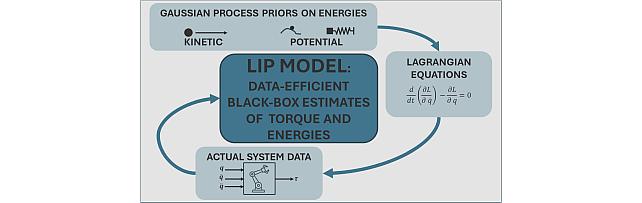
Lagrangian Inspired Polynomial for Robot Inverse Dynamics -
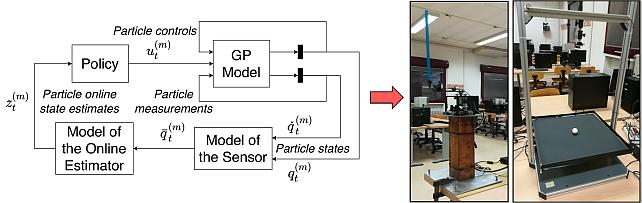
Monte Carlo Probabilistic Inference for Learning COntrol -
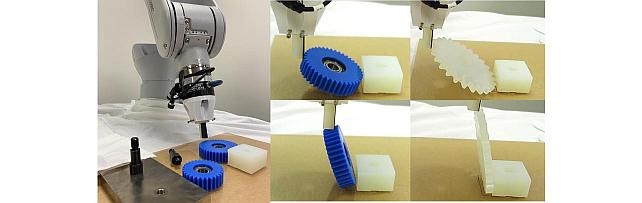
Python-based Robotic Control & Optimization Package -
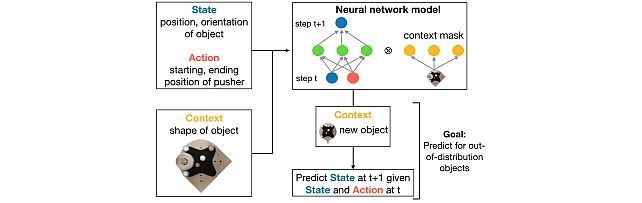
Context-Aware Zero Shot Learning -
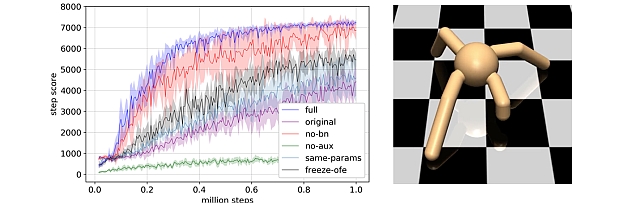
Online Feature Extractor Network -
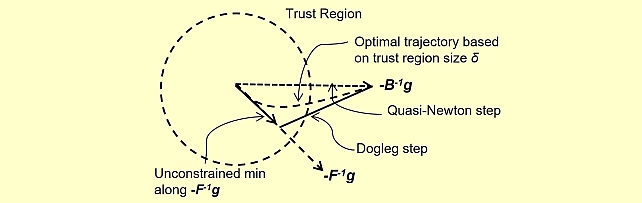
Quasi-Newton Trust Region Policy Optimization -
Circular Maze Environment
-