Artificial Intelligence
Making machines smarter for improved safety, efficiency and comfort.
Our AI research encompasses advances in computer vision, speech and audio processing, as well as data analytics. Key research themes include improved perception based on machine learning techniques, learning control policies through model-based reinforcement learning, as well as cognition and reasoning based on learned semantic representations. We apply our work to a broad range of automotive and robotics applications, as well as building and home systems.
Quick Links
-
Researchers

Jonathan
Le Roux

Toshiaki
Koike-Akino

Ye
Wang

Gordon
Wichern

Anoop
Cherian

Tim K.
Marks

Chiori
Hori

Michael J.
Jones

Kieran
Parsons

Jing
Liu

Daniel N.
Nikovski

Suhas
Lohit

Matthew
Brand

Yoshiki
Masuyama

Kuan-Chuan
Peng

Pu
(Perry)
Wang
Philip V.
Orlik

Diego
Romeres

Moitreya
Chatterjee

Siddarth
Jain

Hassan
Mansour

Petros T.
Boufounos

Radu
Corcodel

William S.
Yerazunis

Pedro
Miraldo

Arvind
Raghunathan

Jianlin
Guo

Hongbo
Sun

Yebin
Wang

Christoph Benedikt Josef
Boeddeker

Chungwei
Lin

Yanting
Ma

Bingnan
Wang

Stefano
Di Cairano

Saviz
Mowlavi

Anthony
Vetro

Jinyun
Zhang

Vedang M.
Deshpande

Christopher R.
Laughman

Dehong
Liu

Alexander
Schperberg

Abraham P.
Vinod

Kenji
Inomata

Kei
Suzuki
-
Awards
-
AWARD MERL team wins the Generative Data Augmentation of Room Acoustics (GenDARA) 2025 Challenge Date: April 7, 2025
Awarded to: Christopher Ick, Gordon Wichern, Yoshiki Masuyama, François G. Germain, and Jonathan Le Roux
MERL Contacts: Jonathan Le Roux; Yoshiki Masuyama; Gordon Wichern
Research Areas: Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, Speech & AudioBrief- MERL's Speech & Audio team ranked 1st out of 3 teams in the Generative Data Augmentation of Room Acoustics (GenDARA) 2025 Challenge, which focused on “generating room impulse responses (RIRs) to supplement a small set of measured examples and using the augmented data to train speaker distance estimation (SDE) models". The team was led by MERL intern Christopher Ick, and also included Gordon Wichern, Yoshiki Masuyama, François G. Germain, and Jonathan Le Roux.
The GenDARA Challenge was organized as part of the Generative Data Augmentation (GenDA) workshop at the 2025 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP 2025), and held on April 7, 2025 in Hyderabad, India. Yoshiki Masuyama presented the team's method, "Data Augmentation Using Neural Acoustic Fields With Retrieval-Augmented Pre-training".
The GenDARA challenge aims to promote the use of generative AI to synthesize RIRs from limited room data, as collecting or simulating RIR datasets at scale remains a significant challenge due to high costs and trade-offs between accuracy and computational efficiency. The challenge asked participants to first develop RIR generation systems capable of expanding a sparse set of labeled room impulse responses by generating RIRs at new source–receiver positions. They were then tasked with using this augmented dataset to train speaker distance estimation systems. Ranking was determined by the overall performance on the downstream SDE task. MERL’s approach to the GenDARA challenge centered on a geometry-aware neural acoustic field model that was first pre-trained on a large external RIR dataset to learn generalizable mappings from 3D room geometry to room impulse responses. For each challenge room, the model was then adapted or fine-tuned using the small number of provided RIRs, enabling high-fidelity generation of RIRs at unseen source–receiver locations. These augmented RIR sets were subsequently used to train the SDE system, improving speaker distance estimation by providing richer and more diverse acoustic training data.
- MERL's Speech & Audio team ranked 1st out of 3 teams in the Generative Data Augmentation of Room Acoustics (GenDARA) 2025 Challenge, which focused on “generating room impulse responses (RIRs) to supplement a small set of measured examples and using the augmented data to train speaker distance estimation (SDE) models". The team was led by MERL intern Christopher Ick, and also included Gordon Wichern, Yoshiki Masuyama, François G. Germain, and Jonathan Le Roux.
-
AWARD MERL Wins Awards at NeurIPS LLM Privacy Challenge Date: December 15, 2024
Awarded to: Jing Liu, Ye Wang, Toshiaki Koike-Akino, Tsunato Nakai, Kento Oonishi, Takuya Higashi
MERL Contacts: Toshiaki Koike-Akino; Jing Liu; Ye Wang
Research Areas: Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, Information SecurityBrief- The Mitsubishi Electric Privacy Enhancing Technologies (MEL-PETs) team, consisting of a collaboration of MERL and Mitsubishi Electric researchers, won awards at the NeurIPS 2024 Large Language Model (LLM) Privacy Challenge. In the Blue Team track of the challenge, we won the 3rd Place Award, and in the Red Team track, we won the Special Award for Practical Attack.
-
AWARD University of Padua and MERL team wins the AI Olympics with RealAIGym competition at IROS24 Date: October 17, 2024
Awarded to: Niccolò Turcato, Alberto Dalla Libera, Giulio Giacomuzzo, Ruggero Carli, Diego Romeres
MERL Contact: Diego Romeres
Research Areas: Artificial Intelligence, Dynamical Systems, Machine Learning, RoboticsBrief- The team composed of the control group at the University of Padua and MERL's Optimization and Robotic team ranked 1st out of the 4 finalist teams that arrived to the 2nd AI Olympics with RealAIGym competition at IROS 24, which focused on control of under-actuated robots. The team was composed by Niccolò Turcato, Alberto Dalla Libera, Giulio Giacomuzzo, Ruggero Carli and Diego Romeres. The competition was organized by the German Research Center for Artificial Intelligence (DFKI), Technical University of Darmstadt and Chalmers University of Technology.
The competition and award ceremony was hosted by IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS) on October 17, 2024 in Abu Dhabi, UAE. Diego Romeres presented the team's method, based on a model-based reinforcement learning algorithm called MC-PILCO.
- The team composed of the control group at the University of Padua and MERL's Optimization and Robotic team ranked 1st out of the 4 finalist teams that arrived to the 2nd AI Olympics with RealAIGym competition at IROS 24, which focused on control of under-actuated robots. The team was composed by Niccolò Turcato, Alberto Dalla Libera, Giulio Giacomuzzo, Ruggero Carli and Diego Romeres. The competition was organized by the German Research Center for Artificial Intelligence (DFKI), Technical University of Darmstadt and Chalmers University of Technology.
See All Awards for Artificial Intelligence -
-
News & Events
-
TALK [MERL Seminar Series 2026] Laixi Shi presents talk titled Robust Decision Making Without Compromising Learning Efficiency Date & Time: Wednesday, January 14, 2026; 1:00 PM
Speaker: Laixi Shi, Johns Hopkins University
MERL Host: Dehong Liu
Research Areas: Artificial Intelligence, Control, Machine LearningAbstract Decision-making artificial intelligence (AI) has revolutionized human life ranging from healthcare, daily life, to scientific discovery. However, current AI systems often lack reliability and are highly vulnerable to small changes in complex, interactive, and dynamic environments. My research focuses on achieving both reliability and learning efficiency simultaneously when building AI solutions. These two goals seem conflicting, as enhancing robustness against variability often leads to more complex problems that requires more data and computational resources, at the cost of learning efficiency. But does it have to?
Decision-making artificial intelligence (AI) has revolutionized human life ranging from healthcare, daily life, to scientific discovery. However, current AI systems often lack reliability and are highly vulnerable to small changes in complex, interactive, and dynamic environments. My research focuses on achieving both reliability and learning efficiency simultaneously when building AI solutions. These two goals seem conflicting, as enhancing robustness against variability often leads to more complex problems that requires more data and computational resources, at the cost of learning efficiency. But does it have to?
In this talk, I overview my work on building reliable decision-making AI without sacrificing learning efficiency, offering insights into effective optimization problem design for reliable AI. To begin, I will focus on reinforcement learning (RL) — a key framework for sequential decision-making, and demonstrate how distributional robustness can be achieved provably without paying statistical premium (additional training data cost) compared to non-robust counterparts. Next, shifting to decision-making in strategic multi-agent systems, I will demonstrate that incorporating realistic risk preferences—a key feature of human decision-making—enables computational tractability, a benefit not present in traditional models. Finally, I will present a vision for building reliable, learning-efficient AI solutions for human-centered applications, though agentic and multi-agentic AI systems.
-
NEWS MERL Researcher Diego Romeres Collaborates with Mitsubishi Electric and University of Padua to Advance Physics-Embedded AI for Predictive Equipment Maintenance Date: December 10, 2025
MERL Contact: Diego Romeres
Research Areas: Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, RoboticsBrief- Mitsubishi Electric Research Laboratories (MERL) researchers, together with collaborators at Mitsubishi Electric’s Information Technology R&D Center in Kamakura, Kanagawa Prefecture, Japan, and the Department of Information Engineering at the University of Padua, have developed a cutting-edge physics-embedded AI technology that substantially improves the accuracy of equipment degradation estimation using minimal training data. This collaborative effort has culminated in a press release by Mitsubishi Electric Corporation announcing the new AI technology as part of its Neuro-Physical AI initiative under the Maisart program.
The interdisciplinary team, including MERL Senior Principal Research Scientist and Team Leader Diego Romeres and University of Padua researchers Alberto Dalla Libera and Giulio Giacomuzzo, combined expertise in machine learning, physical modeling, and real-world industrial systems to embed physics-based models directly into AI frameworks. By training AI with theoretical physical laws and real operational data, the resulting system delivers reliable degradation estimates on the torque of robotic arms even with limited datasets. This result addresses key challenges in preventive maintenance for complex manufacturing environments and supports reduced downtime, maintained quality, and lower lifecycle costs.
The successful integration of these foundational research efforts into Mitsubishi Electric’s business-scale AI solutions exemplifies MERL’s commitment to translating fundamental innovation into real-world impact.
- Mitsubishi Electric Research Laboratories (MERL) researchers, together with collaborators at Mitsubishi Electric’s Information Technology R&D Center in Kamakura, Kanagawa Prefecture, Japan, and the Department of Information Engineering at the University of Padua, have developed a cutting-edge physics-embedded AI technology that substantially improves the accuracy of equipment degradation estimation using minimal training data. This collaborative effort has culminated in a press release by Mitsubishi Electric Corporation announcing the new AI technology as part of its Neuro-Physical AI initiative under the Maisart program.
See All News & Events for Artificial Intelligence -
-
Research Highlights
-
PS-NeuS: A Probability-guided Sampler for Neural Implicit Surface Rendering -
Quantum AI Technology -
TI2V-Zero: Zero-Shot Image Conditioning for Text-to-Video Diffusion Models -
Gear-NeRF: Free-Viewpoint Rendering and Tracking with Motion-Aware Spatio-Temporal Sampling -
Private, Secure, and Reliable Artificial Intelligence -
Steered Diffusion -
Sustainable AI -
Robust Machine Learning -
mmWave Beam-SNR Fingerprinting (mmBSF) -
Video Anomaly Detection -
Biosignal Processing for Human-Machine Interaction -
Task-aware Unified Source Separation - Audio Examples
-
-
Internships
-
OR0249: Internship - Whole-body manipulation for quadrupedal robots
-
OR0239: Internship - Robot Learning and Perception for Disassembly
-
CV0224: Internship - Language-Guided Human-Robot Interaction
See All Internships for Artificial Intelligence -
-
Openings
See All Openings at MERL -
Recent Publications
- , "Amplification Effects in Test-Time Reinforcement Learning: Safety and Reasoning Vulnerabilities", AAAI Workshop on Trust and Control in Agentic AI, January 2026.BibTeX TR2026-020 PDF
- @inproceedings{Khattar2026jan,
- author = {Khattar, Vanshaj and Choudhury, Moumita and Rashid, Md Rafi Ur and Liu, Jing and Koike-Akino, Toshiaki and Jin, Ming and Wang, Ye},
- title = {{Amplification Effects in Test-Time Reinforcement Learning: Safety and Reasoning Vulnerabilities}},
- booktitle = {AAAI Workshop on Trust and Control in Agentic AI},
- year = 2026,
- month = jan,
- url = {https://www.merl.com/publications/TR2026-020}
- }
- , "LatentLLM: Activation-Aware Transform to Multi-Head Latent Attention", AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, January 2026.BibTeX TR2026-018 PDF Presentation
- @inproceedings{Koike-Akino2026jan,
- author = {{{Koike-Akino, Toshiaki and Chen, Xiangyu and Liu, Jing and Wang, Ye and Wang, Pu and Brand, Matthew}}},
- title = {{{LatentLLM: Activation-Aware Transform to Multi-Head Latent Attention}}},
- booktitle = {AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence},
- year = 2026,
- month = jan,
- url = {https://www.merl.com/publications/TR2026-018}
- }
- , "Chain-of-Thought Driven Adversarial Scenario Extrapolation for Robust Language Models", AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, January 2026.BibTeX TR2026-017 PDF
- @inproceedings{Rashid2026jan,
- author = {Rashid, Md Rafi Ur and Dasu, Vishnu Asutosh and Wang, Ye and Tan, G. Gary and Mehnaz, Shagufta},
- title = {{Chain-of-Thought Driven Adversarial Scenario Extrapolation for Robust Language Models}},
- booktitle = {AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence},
- year = 2026,
- month = jan,
- url = {https://www.merl.com/publications/TR2026-017}
- }
- , "Embracing Cacophony: Explaining and Improving Random Mixing in Music Source Separation", IEEE Open Journal of Signal Processing, DOI: 10.1109/OJSP.2025.3633567, Vol. 6, pp. 1179-1192, January 2026.BibTeX TR2026-012 PDF
- @article{Jeon2026jan,
- author = {Jeon, Chang-Bin and Wichern, Gordon and Germain, François G and {Le Roux}, Jonathan},
- title = {{Embracing Cacophony: Explaining and Improving Random Mixing in Music Source Separation}},
- journal = {IEEE Open Journal of Signal Processing},
- year = 2026,
- volume = 6,
- pages = {1179--1192},
- month = jan,
- doi = {10.1109/OJSP.2025.3633567},
- url = {https://www.merl.com/publications/TR2026-012}
- }
- , "Local Density-Based Anomaly Score Normalization for Domain Generalization", IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech and Language Processing, January 2026.BibTeX TR2026-010 PDF Software
- @article{Wilkinghoff2026jan,
- author = {Wilkinghoff, Kevin and Yang, Haici and Ebbers, Janek and Germain, François G and Wichern, Gordon and {Le Roux}, Jonathan},
- title = {{Local Density-Based Anomaly Score Normalization for Domain Generalization}},
- journal = {IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech and Language Processing},
- year = 2026,
- month = jan,
- url = {https://www.merl.com/publications/TR2026-010}
- }
- , "Recent Trends in Distant Conversational Speech Recognition: A Review of CHiME-7 and 8 DASR Challenges", Computer Speech & Language, DOI: 10.1016/j.csl.2025.101901, Vol. 97, pp. 101901, December 2025.BibTeX TR2026-008 PDF
- @article{Cornell2025dec,
- author = {Cornell, Samuele and Boeddeker, Christoph and Park, Taejin and Huang, He and Raj, Desh and Wiesner, Matthew and Masuyama, Yoshiki and Chang, Xuankai and Wang, Zhong-Qiu and Squartini, Stefano and Garcia, Paola and Watanabe, Shinji},
- title = {{Recent Trends in Distant Conversational Speech Recognition: A Review of CHiME-7 and 8 DASR Challenges}},
- journal = {Computer Speech \& Language},
- year = 2025,
- volume = 97,
- pages = 101901,
- month = dec,
- doi = {10.1016/j.csl.2025.101901},
- url = {https://www.merl.com/publications/TR2026-008}
- }
- , "SuDaField: Subject- and Dataset-Aware Neural Field for HRTF Modeling", IEEE Open Journal of Signal Processing, DOI: 10.1109/OJSP.2025.3627073, Vol. 6, pp. 1169-1178, December 2025.BibTeX TR2026-009 PDF
- @article{Masuyama2025dec2,
- author = {Masuyama, Yoshiki and Wichern, Gordon and Germain, François G and Ick, Christopher and {Le Roux}, Jonathan},
- title = {{SuDaField: Subject- and Dataset-Aware Neural Field for HRTF Modeling}},
- journal = {IEEE Open Journal of Signal Processing},
- year = 2025,
- volume = 6,
- pages = {1169--1178},
- month = dec,
- doi = {10.1109/OJSP.2025.3627073},
- url = {https://www.merl.com/publications/TR2026-009}
- }
- , "RANF: Neural Field-Based HRTF Spatial Upsampling with Retrieval Augmentation and Parameter Efficient Fine-Tuning", IEEE Open Journal of Signal Processing, DOI: 10.1109/OJSP.2025.3640517, Vol. 7, pp. 32-41, December 2025.BibTeX TR2026-007 PDF Software
- @article{Masuyama2025dec,
- author = {Masuyama, Yoshiki and Wichern, Gordon and Germain, François G and Ick, Christopher and {Le Roux}, Jonathan},
- title = {{RANF: Neural Field-Based HRTF Spatial Upsampling with Retrieval Augmentation and Parameter Efficient Fine-Tuning}},
- journal = {IEEE Open Journal of Signal Processing},
- year = 2025,
- volume = 7,
- pages = {32--41},
- month = dec,
- doi = {10.1109/OJSP.2025.3640517},
- url = {https://www.merl.com/publications/TR2026-007}
- }
- , "Amplification Effects in Test-Time Reinforcement Learning: Safety and Reasoning Vulnerabilities", AAAI Workshop on Trust and Control in Agentic AI, January 2026.
-
Videos
-
Software & Data Downloads
-
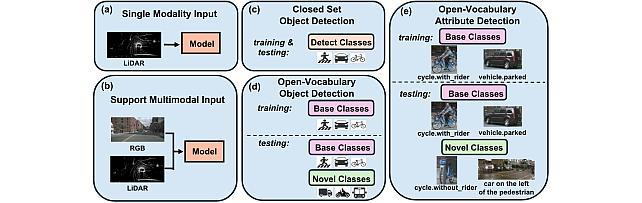
Open Vocabulary Attribute Detection Dataset -
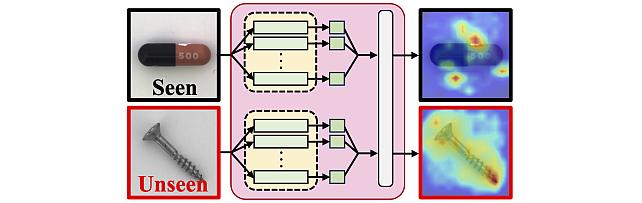
Long-Tailed Online Anomaly Detection dataset -
Group Representation Networks -
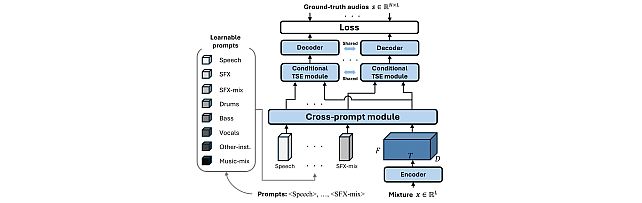
Task-Aware Unified Source Separation -
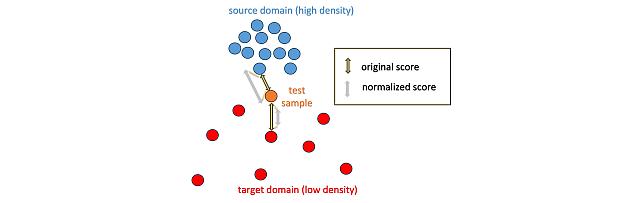
Local Density-Based Anomaly Score Normalization for Domain Generalization -
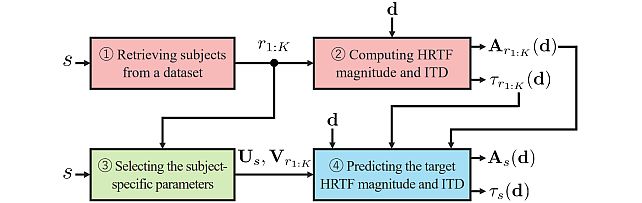
Retrieval-Augmented Neural Field for HRTF Upsampling and Personalization -
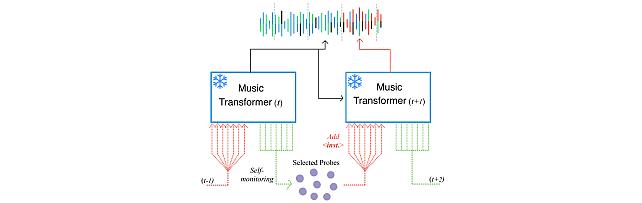
Self-Monitored Inference-Time INtervention for Generative Music Transformers -
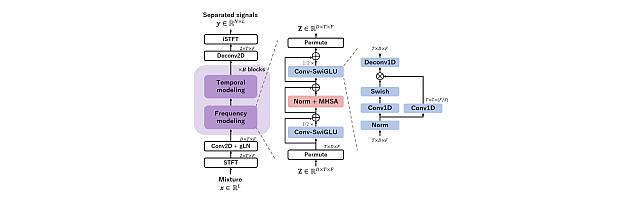
Transformer-based model with LOcal-modeling by COnvolution -
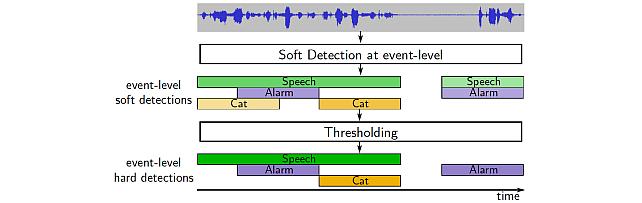
Sound Event Bounding Boxes -
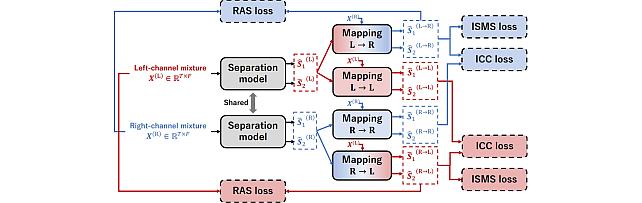
Enhanced Reverberation as Supervision -

Zero-Shot Image Conditioning for Text-to-Video Diffusion Models -
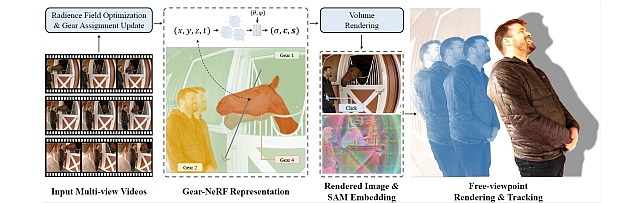
Gear Extensions of Neural Radiance Fields -
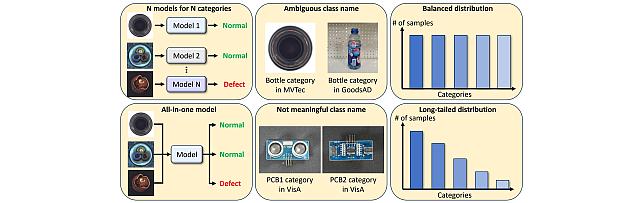
Long-Tailed Anomaly Detection Dataset -
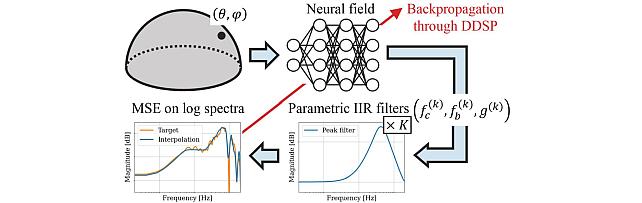
Neural IIR Filter Field for HRTF Upsampling and Personalization -
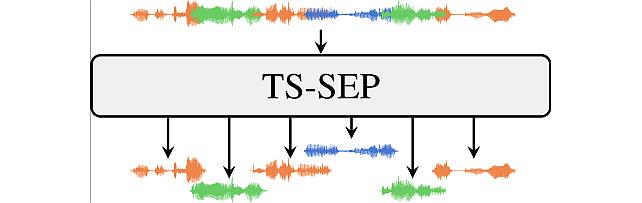
Target-Speaker SEParation -

Pixel-Grounded Prototypical Part Networks -

Steered Diffusion -
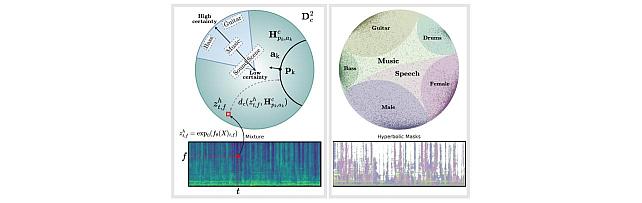
Hyperbolic Audio Source Separation -

Simple Multimodal Algorithmic Reasoning Task Dataset -
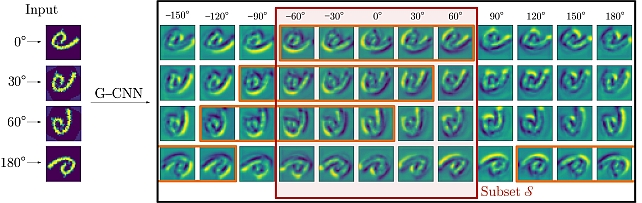
Partial Group Convolutional Neural Networks -
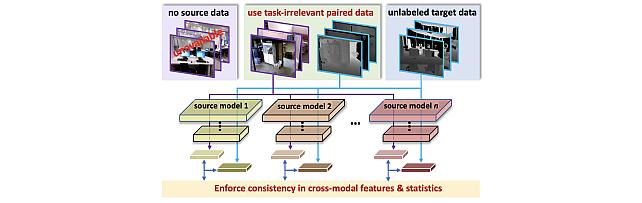
SOurce-free Cross-modal KnowledgE Transfer -
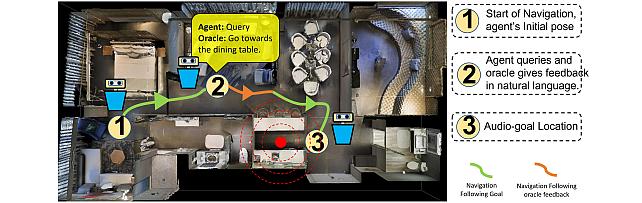
Audio-Visual-Language Embodied Navigation in 3D Environments -
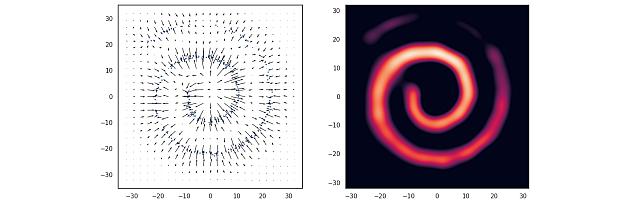
Nonparametric Score Estimators -
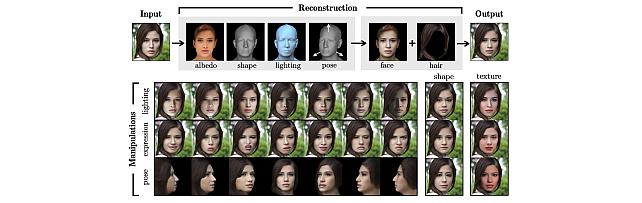
3D MOrphable STyleGAN -
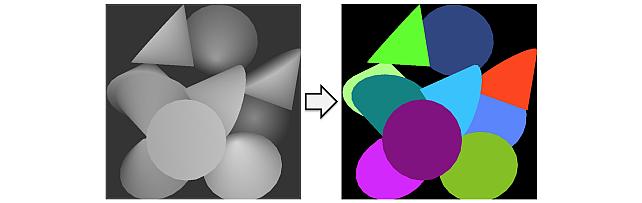
Instance Segmentation GAN -
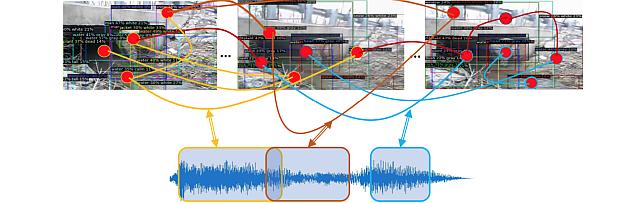
Audio Visual Scene-Graph Segmentor -
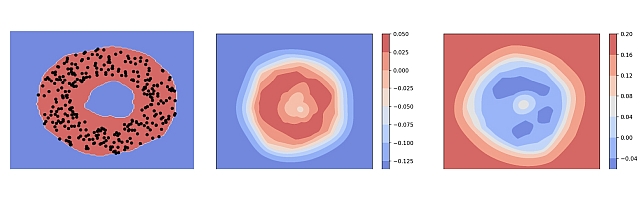
Generalized One-class Discriminative Subspaces -
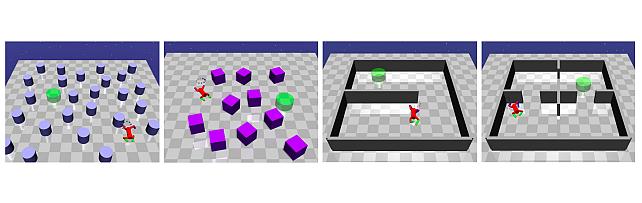
Goal directed RL with Safety Constraints -
Hierarchical Musical Instrument Separation -
Generating Visual Dynamics from Sound and Context -

Adversarially-Contrastive Optimal Transport -
Online Feature Extractor Network -
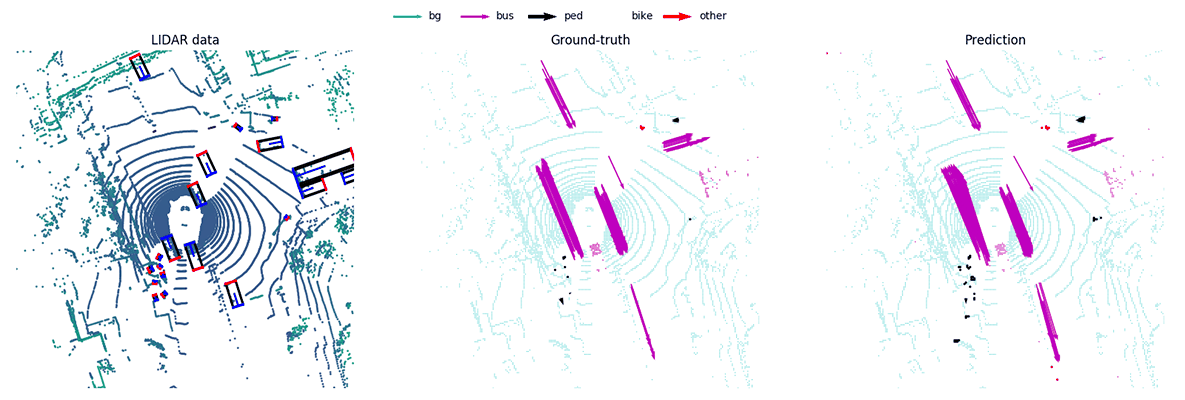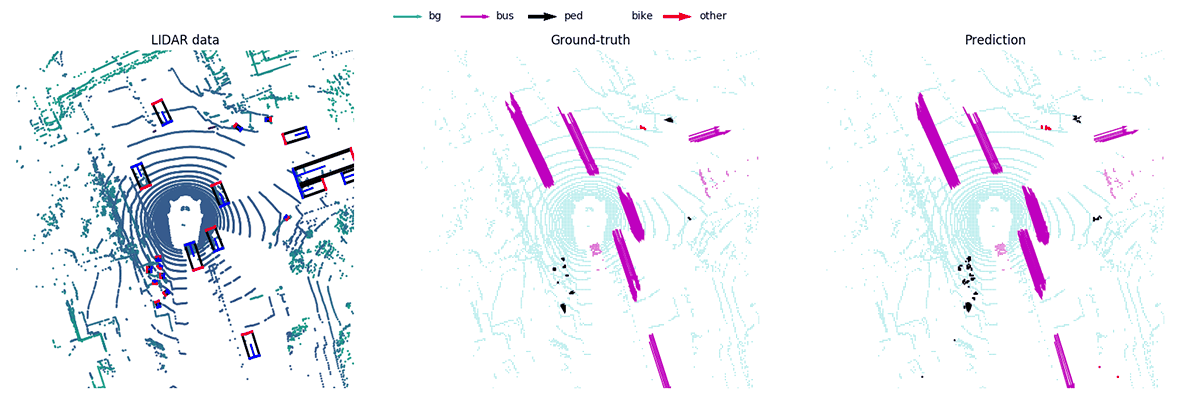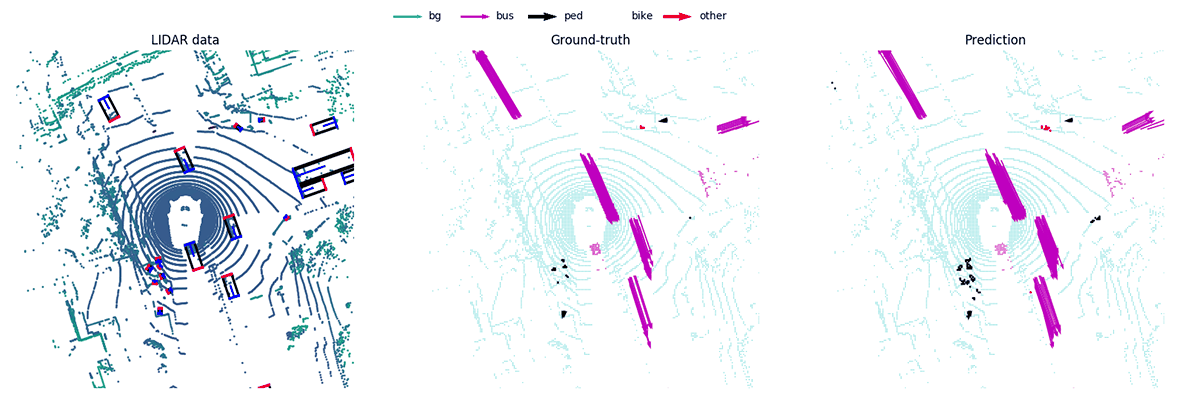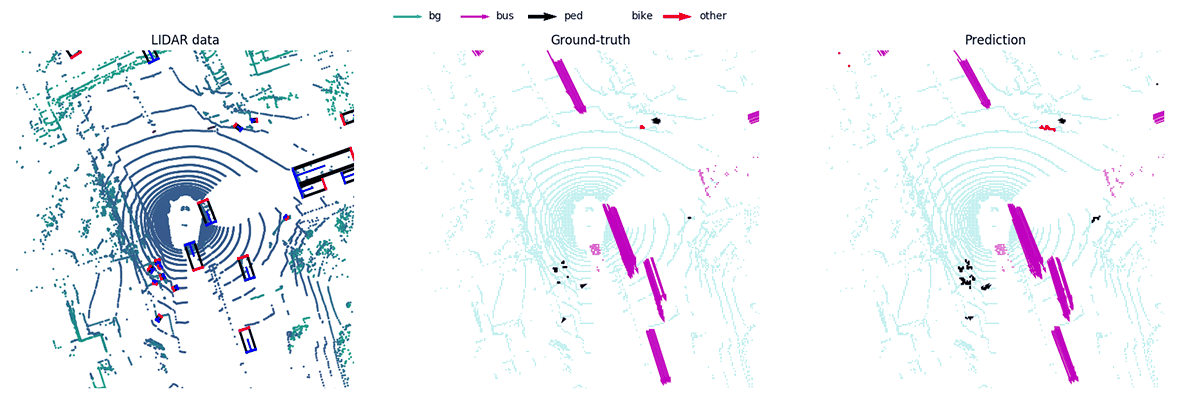
MotionNet -
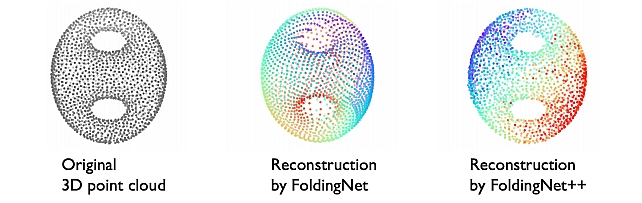
FoldingNet++ -
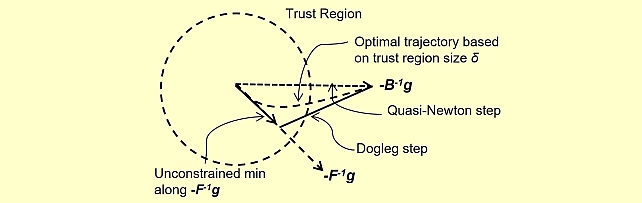
Quasi-Newton Trust Region Policy Optimization -
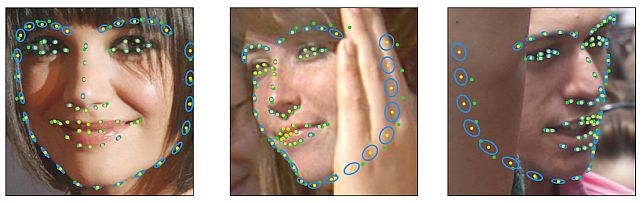
Landmarks’ Location, Uncertainty, and Visibility Likelihood -
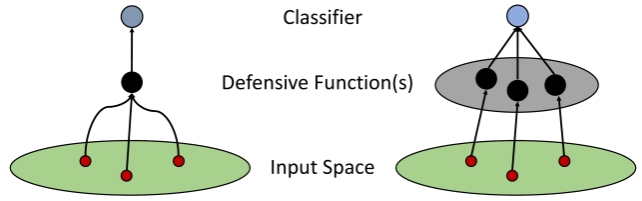
Robust Iterative Data Estimation -
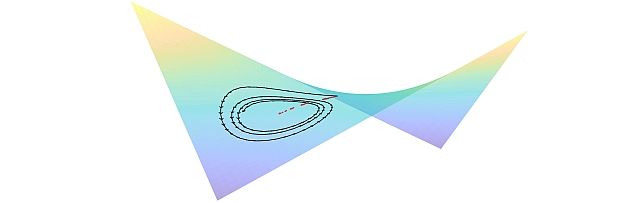
Gradient-based Nikaido-Isoda -
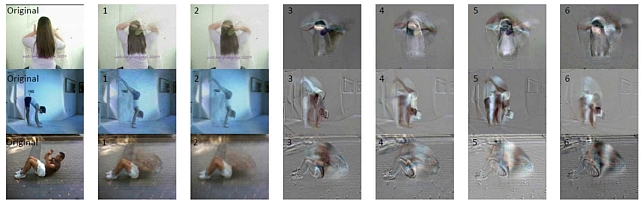
Discriminative Subspace Pooling -
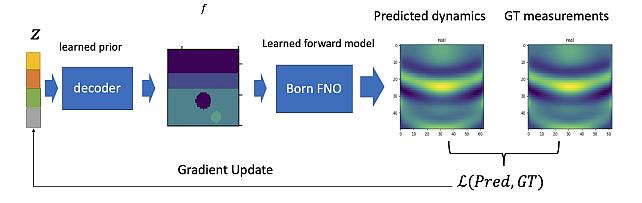
Learned Born Operator for Reflection Tomographic Imaging -

MEL-PETs Defense for LLM Privacy Challenge -
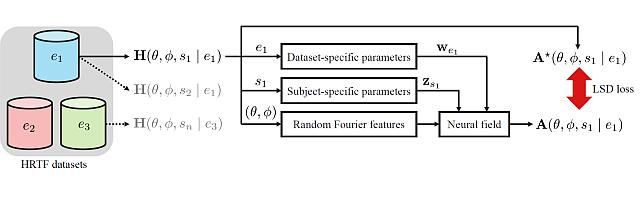
Subject- and Dataset-Aware Neural Field for HRTF Modeling -
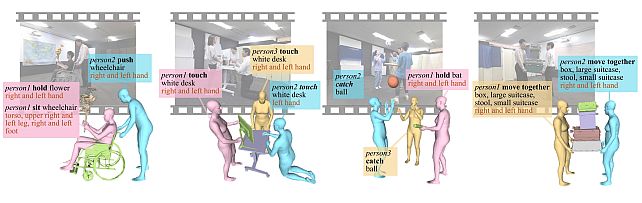
MMHOI Dataset: Modeling Complex 3D Multi-Human Multi-Object Interactions -

MEL-PETs Joint-Context Attack for LLM Privacy Challenge
-