TR2020-141
Efficient Exploration in Constrained Environments with Goal-Oriented Reference Path
-
- , "Efficient Exploration in Constrained Environments with Goal-Oriented Reference Path", IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), November 2020.BibTeX TR2020-141 PDF Software
- @inproceedings{Ota2020nov,
- author = {Ota, Kei and Sasaki, Yoko and Jha, Devesh and Yoshiyasu, Yusuke and Kanezaki, Asako},
- title = {{Efficient Exploration in Constrained Environments with Goal-Oriented Reference Path}},
- booktitle = {IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS)},
- year = 2020,
- month = nov,
- url = {https://www.merl.com/publications/TR2020-141}
- }
- , "Efficient Exploration in Constrained Environments with Goal-Oriented Reference Path", IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), November 2020.
-
Research Area:
Abstract:
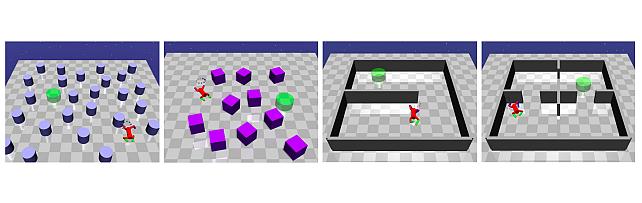
In this paper, we consider the problem of building learning agents that can efficiently learn to navigate in constrained environments. The main goal is to design agents that can efficiently learn to understand and generalize to different environments using high-dimensional inputs (a 2D map), while following feasible paths that avoid obstacles in obstacle-cluttered environment. To achieve this, we make use of traditional path planning algorithms, supervised learning, and reinforcement learning algorithms in a synergistic way. The key idea is to decouple the navigation problem into planning and control, the former of which is achieved by supervised learning whereas the latter is done by reinforcement learning. Specifically, we train a deep convolutional network that can predict collision-free paths based on a map of the environment– this is then used by an reinforcement learning algorithm to learn to closely follow the path. This allows the trained agent to achieve good generalization while learning faster. We test our proposed method in the recently proposed Safety Gym suite that allows testing of safety-constraints during training of learning agents. We compare our proposed method with existing work and show that our method consistently improves the sample efficiency and generalization capability to novel environments.