TR2008-057
Towards a 3D Video Format for Auto-Stereoscopic Displays
-
- , "Towards a 3D Video Format for Auto-Stereoscopic Displays", SPIE Conference on Applications of Digital Image Processing, September 2008, vol. 7073.BibTeX TR2008-057 PDF
- @inproceedings{Vetro2008aug,
- author = {Vetro, A. and Yea, S. and Smolic, A.},
- title = {{Towards a 3D Video Format for Auto-Stereoscopic Displays}},
- booktitle = {SPIE Conference on Applications of Digital Image Processing},
- year = 2008,
- volume = 7073,
- month = aug,
- url = {https://www.merl.com/publications/TR2008-057}
- }
- , "Towards a 3D Video Format for Auto-Stereoscopic Displays", SPIE Conference on Applications of Digital Image Processing, September 2008, vol. 7073.
-
MERL Contact:
-
Research Area:
Digital Video
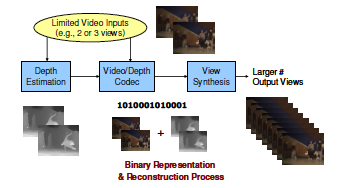
Abstract:
There has been increased momentum recently in the production of 3D content for cinema applications; for the most part, this has been limited to stereo content. There are also a variety of display technologies on the market that support 3DTV, each offering a different viewing experience and having different input requirements. More specifically, stereoscopic displays support stereo content and require glasses, while auto-stereoscopic displays avoid the need for glasses by rending view-dependent stereo pairs for a multitude of viewing angles. To realize high quality auto-stereoscopic displays, multiple views of the video must either be provided as input to the display, or these views must be created locally at the display. The former approach has difficulties in that the production environment is typically limited to stereo, and transmission bandwidth for a large number of views is not likely to be available. This paper discusses an emerging 3D data format that enables the latter approach to be realized. A new framework for efficiently representing a 3D scene and enabling the reconstruction of an arbitrarily large number of views prior to rendering is introduced. Several design challenges are also highlighted through experimental results.
Related News & Events
-
NEWS SPIE Conference on Applications of Digital Image Processing 2008: publication by Anthony Vetro, Sehoon Yea and others Date: August 11, 2008
Where: SPIE Conference on Applications of Digital Image Processing
MERL Contact: Anthony Vetro
Research Area: Digital VideoBrief- The paper "Towards a 3D Video Format for Auto-Stereoscopic Displays" by Vetro, A., Yea, S. and Smolic, A. was presented at the SPIE Conference on Applications of Digital Image Processing.
